Dancing in the Kingdom- Table of Contents
Dancing In the Kingdom – Part 2 – The Kingdom Revealed – Chapter 13 – Distinctives within the body of Christ
The Challenge of the church
[Bible references: 2 Corinthians 11:1-15; Galatians 2:7; Colossians 2:8; 2 Thessalonians 2:4-15; 1 Timothy 2:14-26; 6:11-21; 2 Timothy 1:12-14; 2:16; 3:14-16]
Mysteries and distinctives
There is an impossible task set before the believers through the world who comprise what some call the invisible, universal church: Differences have arisen which have caused different local congregations to have some disagreements about what the correct theology is. We will call these differences, distinctives. It is from these distinctives that local congregations divide from one another with some finding themselves aligned into different groups that we call denominations or associations, and some not formally aligning themselves with any other congregation at all.
Although while trying to understand God, we may find that although some things are incomprehensible, other things are knowable. The knowable things make it possible to construct a limited theological framework, despite the tensions cited in Chapter 2 that require us to hold some things in tension.
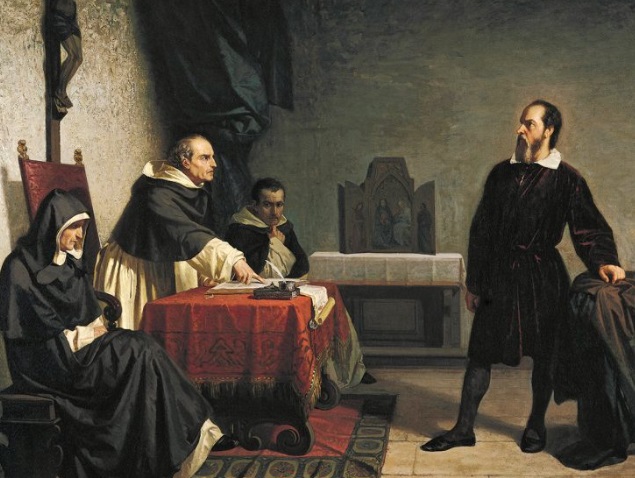
When distinctives become heresies
Trying to understand a complex, incomprehensible and paradoxical God leads naturally to some diversity of thought. The problem is trying to detect when diversity leads to heresies, ideas that are identifiably contrary to the Biblical message and ought to be rejected by all the major bodies in the church. Heresies typically develop when biblical verses are taken out of context, or when attempts are made to mesh non-Christian ideas with biblical ideas.
The following is a list of some of the most prevalent heresies. For a more comprehensive list of some of the heresies and the terms used for them, read “Appendix F – Partial Listing of Heresies”.:
- Matter is inherently evil and only the spiritual is good,
- being saved by grace allows us to ignore any laws or norms,
- rejection of the Old Testament,
- rejection of the Trinity,
- only the Father is God,
- Gentiles need to be circumcised and follow the Jewish laws,
- the validity of sacraments depends on the moral character of the person administering the sacraments,
- those guilty of grave sin are permanently excluded from the church,
- we can choose to be good apart from God’s grace,
- Christ is not fully human and fully divine,
- prophets who claim that they supersede the apostles,
- all truth and knowledge of God is accessible by the human mind.,
- all people will be saved.
Even within our limited framework, it is possible to find that sometimes someone’s theology seems so wrong that it must be corrected and dealt with more strongly. In those cases, the church must determine when some of our distinctives have crossed over from being a ‘distinctive’ to being a ‘heresy,’ teachings that are not just different but cause fundamental theological problems in the teachings of the church. The task of identifying and correcting heresies is a job that must be done but these days is complicated by the divisions within the church. This is one area where we need to recognize Dynamic Tension at work: balancing the need to deal with doctrine and practices that are deemed to be heretical with the need to, as much as possible, retain whatever unity is possible in the church.
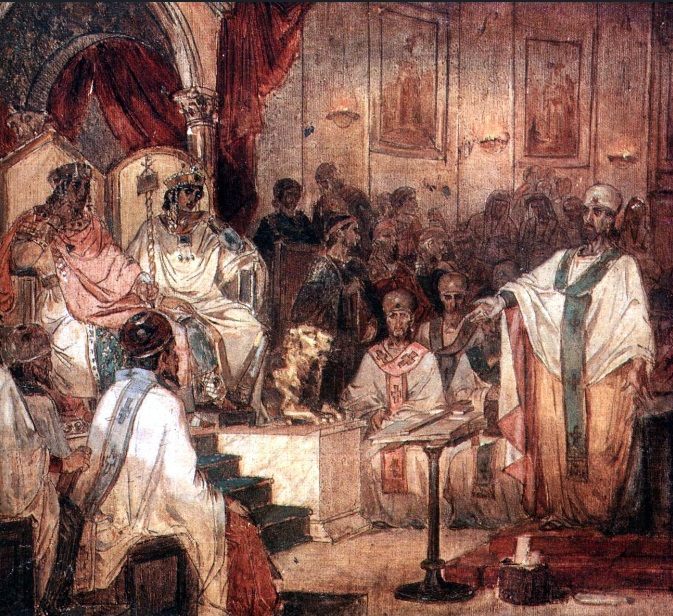
There was a time that it was more possible to call together representatives from all parts of the church to discuss difficult issues and come to a common agreement, but that is no longer possible. Between AD325 and AD757 there were seven ecumenical councils[1], councils that were called by the Roman emperor which tried to resolve various questions, at least within the empire, which were dividing the church.
“all the doctrinal definitions of the Seven Ecumenical Councils (councils which have always, and still do, receive the unqualified acceptance of both East and West) … An Ecumenical Synod may be defined as a synod the decrees of which have found acceptance by the Church in the whole world”[2]
One of the most essential products of the councils were increasingly detailed creeds[3] for the church, statements written in response to perceived heresies that were being taught, clarifying what the orthodox teaching of the church ought to be.
Because of the complexities of the different viewpoints, the increasingly detailed creeds were never able to entirely resolve the differences between the Latin speaking and the Greek speaking parts of the church leaving the church with very intense divisions in the aftermath of each of the councils. After the seven Ecumenical Councils, the divisions in the church had become irreconcilable and it is no longer possible to call a council in which all sections of the church would be able to have an agreement on critical theological issues. There have been various ecumenical efforts through the years, including the creation of the World Council of Churches, but such efforts have not been able to overcome those disagreements on critical issues.
This division has complicated the issue of when theological differences become heresies. The inability of the visible church to resolve such issues forces us acknowledge our dependence on Christ; that the Gospel is the good news about our salvation to be found in the grace of Christ – and not in His still fractured church. In the meanwhile, despite the visible fracturing of the visible church, we need to humbly acknowledge the mystery of the unity of the church in Christ.
[1] Orthodox Church of America. “The Councils” Volume I – Doctrine and Scripture, Sources of Christian Doctrine, The Councils www.oca.org/orthodoxy/the-orthodox-faith/doctrine-scripture/sources-of-christian-doctrine/the-councils; Keating, Karl. “The 21 Ecumenical Councils” Catholic Answers www.catholic.com/magazine/print-edition/the-21-ecumenical-councils. Protestants and Eastern Orthodox regard only 7 ecumenical council, while the Roman Catholic regards 21 ecumenical councils because the Roman Catholic Church regards Eastern Orthodox and Protestant Churches as “separated brethren”.
[2] Schaff, Philip (1819-1893) (Editor) Publisher: Grand Rapids, MI: Christian Classics Ethereal Library, “A select library of the Nicene and Post-Nicene Fathers of the Christian Church. Second Series. Volume XIV. The Seven Ecumenical Councils. For a summary of the seven ecumenical Councils, See Appendix H
[3] See Appendix I – Creeds of the Church
Observe
Read 2 Corinthians 11:1-15; 1 Timothy 4:1-4; 6:1-10; 2 Timothy 2: 14-26. What are the warning signs of “false teachers?”